Which of the following topologies is a type of physical network design where each computer in the network is connected to a central device through an unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) wire?
- Mesh topology
- Star topology
- Ring topology
- Bus topology
Answer(s): B
Explanation:
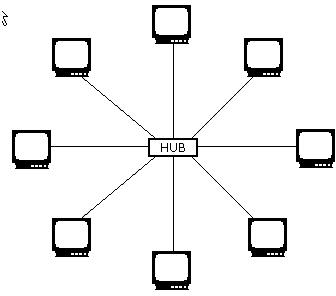
Star topology is a type of physical network design where each computer in the network is connected to a central device, called hub, through an unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) wire. Signals from the sending computer go to the hub and are then transmitted to all the computers in the network. Since each workstation has a separate connection to the hub, it is easy to troubleshoot. Currently, it is the most popular topology used for networks.
Star Topology:
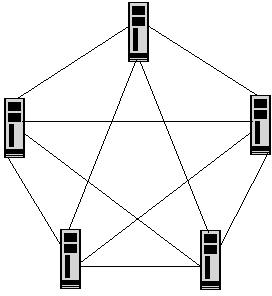
Answer option A is incorrect. Mesh network topology is a type of physical network design where all devices in a network are connected to each other with many redundant connections. It provides multiple paths for the data traveling on the network to reach its destination. Mesh topology also provides redundancy in the network. It employs the full mesh and partial mesh methods to connect devices. In a full mesh topology network, each computer is connected to all the other computers. In a partial mesh topology network, some of the computers are connected to all the computers, whereas some are connected to only those computers with which they frequently exchange data.
Mesh Topology:
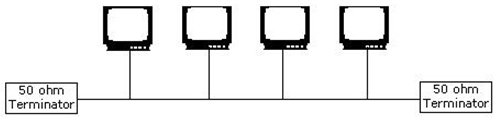
Answer option D is incorrect. Bus topology is a type of physical network design where all computers in the network are connected through a single coaxial cable known as bus. This topology uses minimum cabling and is therefore, the simplest and least expensive topology for small networks. In this topology, 50 ohm terminators terminate both ends of the network. A Bus topology network is difficult to troubleshoot, as a break or problem at any point along the cable can cause the entire network to go down.
Bus Topology:
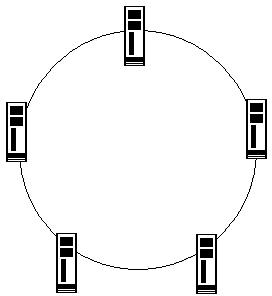
Answer option C is incorrect. Ring topology is a type of physical network design where all computers in the network are connected in a closed loop. Each computer or device in a Ring topology network acts as a repeater. It transmits data by passing a token around the network in order to prevent the collision of data between two computers that want to send messages at the same time. If a token is free, the computer waiting to send data takes it, attaches the data and destination address to the token, and sends it. When the token reaches its destination computer, the data is copied. Then, the token gets back to the originator. The originator finds that the message has been copied and received and removes the message from the token. Now, the token is free and can be used by the other computers in the network to send data. In this topology, if one computer fails, the entire network goes down.
Ring Topology: