Case Study
This is a case study. Case studies are not timed separately. You can use as much exam time as you would like to complete each case. However, there may be additional case studies and sections on this exam. You must manage your time to ensure that you are able to complete all questions included on this exam in the time provided.
To answer the questions included in a case study, you will need to reference information that is provided in the case study. Case studies might contain exhibits and other resources that provide more information about the scenario that is described in the case study. Each question is independent of the other questions in this case study.
At the end of this case study, a review screen will appear. This screen allows you to review your answers and to make changes before you move to the next section of the exam. After you begin a new section, you cannot return to this section.
To start the case study
To display the first question in this case study, click the Next button. Use the buttons in the left pane to explore the content of the case study before you answer the questions. Clicking these buttons displays information such as business requirements, existing environment, and problem statements. If the case study has an All Information tab, note that the information displayed is identical to the information displayed on the subsequent tabs.
When you are ready to answer a question, click the Question button to return to the question.
Overview
ADatum Corporation is a financial services company that has a main office in New York City.
Existing Environment. Licensing Agreement
ADatum has a Microsoft Volume Licensing agreement that includes Software Assurance.
Existing Environment. Network Infrastructure
ADatum has an on-premises datacenter and an Azure subscription named Sub1.
Sub1 contains a virtual network named Network1 in the East US Azure region.
The datacenter is connected to Network1 by using a Site-to-Site (S2S) VPN.
Existing Environment. Identity Environment
The on-premises network contains an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forest.
The forest contains a single domain named corp.adatum.com.
The corp.adatum.com domain syncs with a Microsoft Entra tenant named adatum.com.
Existing Environment. Database Environment
The datacenter contains the servers shown in the following table.
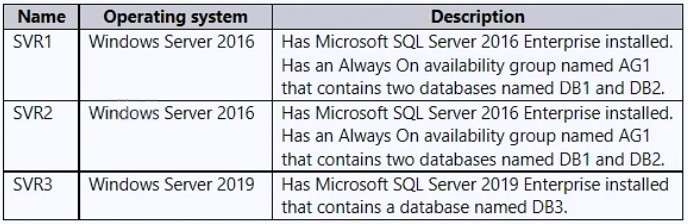
DB1 and DB2 are used for transactional and analytical workloads by an application named App1.
App1 runs on Microsoft Entra hybrid joined servers that run Windows Server 2022. App1 uses Kerberos authentication.
DB3 stores compliance data used by two applications named App2 and App3.
DB3 performance is monitored by using Extended Events sessions, with the event_file target set to a file share on a local disk of SVR3.
Resource allocation for DB3 is managed by using Resource Governor.
Requirements. Planned Changes
ADatum plans to implement the following changes:
Deploy an Azure SQL managed instance named Instance1 to Network1.
Migrate DB1 and DB2 to Instance1.
Migrate DB3 to Azure SQL Database.
Following the migration of DB1 and DB2, hand over database development to remote developers who use
Microsoft Entra joined Windows 11 devices.
Following the migration of DB3, configure the database to be part of an auto-failover group.
Requirements. Availability Requirements
ADatum identifies the following post-migration availability requirements:
For DB1 and DB2, offload analytical workloads to a read-only database replica in the same Azure region.
Ensure that if a regional disaster occurs, DB1 and DB2 can be recovered from backups.
After the migration, App1 must maintain access to DB1 and DB2.
For DB3, manage potential performance issues caused by resource demand changes by App2 and App3.
Ensure that DB3 will still be accessible following a planned failover.
Ensure that DB3 can be restored if the logical server is deleted.
Minimize downtime during the migration of DB1 and DB2.
Requirements. Security Requirements
ADatum identifies the following security requirements for after the migration:
Ensure that only designated developers who use Microsoft Entra joined Windows 11 devices can access
DB1 and DB2 remotely.
Ensure that all changes to DB3, including ones within individual transactions, are audited and recorded.
Requirements. Management Requirements
ADatum identifies the following post-migration management requirements:
Continue using Extended Events to monitor DB3.
In Azure SQL Database, automate the management of DB3 by using elastic jobs that have database-scoped credentials.
Requirements. Business Requirements
ADatum identifies the following business requirements:
Minimize costs whenever possible, without affecting other requirements.
Minimize administrative effort.