Facing fiercer competition at home and abroad, IKEA, the leading furniture retailer, needs to im- prove its competitiveness. In order to do this, IKEA must decrease operating costs and improve quality of current and new retail stores. The company establishes a project team. The job of the team is to collect data on performance from multiple stores in several countries, then select the best performing one. The team will work closely with best performing store and study its processes. After the research, the team will recommend best practices to other retail stores. IKEA management can also apply these practices to new stores in the future.
Which of the following correctly describe the process undertaken by IKEA project team?
- Internal benchmarking
- Competitive benchmarking
- Internal audit
- Site visit
Answer(s): A
Explanation:
Basically, IKEA project team is undertaking the following process:
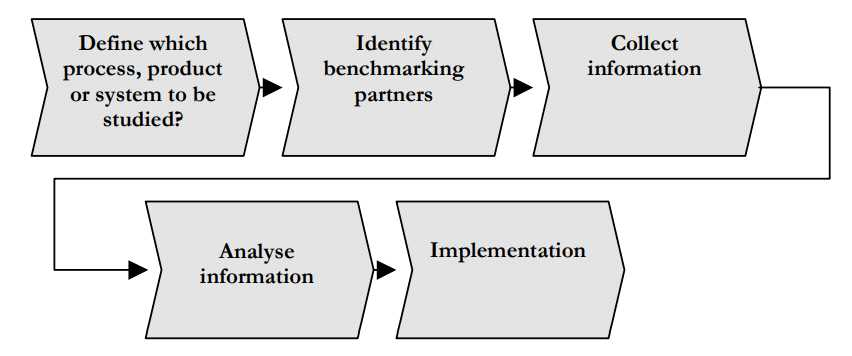
This is a typical benchmarking process. Benchmarking is defined as the process of measuring products, services, and processes against those of organizations known to be leaders in one or more aspects of their operations. Benchmarking provides necessary insights to help you understand how your organization compares with similar organizations, even if they are in a different business or have a different group of customers.
In the scenario, benchmarking process is undertaken within subsidiaries of IKEA, thus it is internal.
Reference:
- CIPS study guide page 49-51
- What is Benchmarking? Technical & Competitive Benchmarking Process | ASQ
- Internal Benchmarking at IKEA
LO 1, AC 1.3