Explanation:
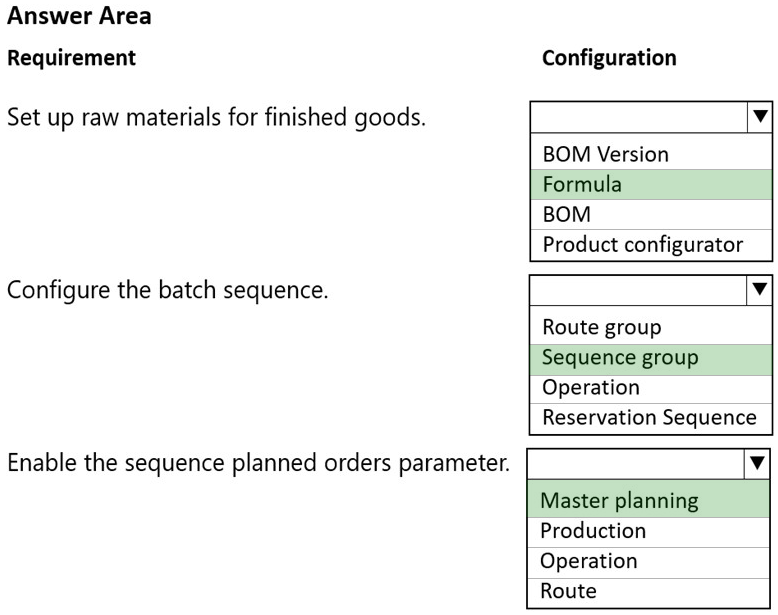
Box 1: Formula
Set up raw materials for finished goods
Formulas, though conceptually similar to BOMs, have a few key distinctions. A few of these differences are outlined below:
Unlike BOMs, Formulas are generally used by process manufacturers
Formulas are commonly used in Batch order rather than Production orders
Instead of consisting of “components”, Formulas more often combine different measurements of certain “ingredients”
Since these ingredients are combined, items that are created from a formula cannot easily be broken down into the original ingredients
Depending on other factors (order size, raw materials available, etC. ), a formula can be scaled up or scaled down
Formulas allow the use of co-products and by-products
Formula lines can be allocated on a percentage basis vs designated quantities
Formulas permit the utilization of catch weight items
What defines an item created from a formula is that each of the ingredients are fully consumed and transformed into a new item. You cannot break an item that is created from a formula back into its original components. Think of using a formula for a production item like following a recipe to bake a cake. Once the ingredients are combined and the cake is baked, it would be very difficult to break the cake back down into flour, eggs, sugar, etC. The same goes for companies that use formulas to produce items such as paper or plastiC.
Incorrect:
* BOM
In the simplest terms, a BOM is a list of components (such as raw materials and sub-assemblies) required to produce a finished gooD. Items created from a BOM can usually be disassembled into the original components; generally, these items are not consumed or transformed in the production process. For this reason, BOMs are more common among discrete manufacturers than process manufacturers. Some examples of items that might be created from BOMs are chairs, desks, and manufacturing equipment. A BOM for a desk might look like:
4 legs
1 table top
4 drawers
18 screws
Box 2: Sequence group
Configure the batch sequence
About batch order sequencing
You can use batch order sequencing to define sequences that you can assign to items. A sequence is an item characteristic that is used to sort items in groups so that the items with similar characteristics are scheduled for production together.
You can perform the following tasks for batch order sequencing:
* Create a sequence group and assign sequences to the sequence group.
* Assign a sequence group to an operation resource or resource group.
* EtC.
Note: Set up sequence groups
Use this procedure to create sequence groups that are used to schedule production. You can assign sequences to a sequence group and then rank these sequences in the order of preference. For example, in the paint industry, color-based paints can have color properties and other attributes, such as latex or enamel. You can create a sequence that contains values for colors that are ranked according to preference in which these colors are ordered or sorteD. You can create another sequence that contains values for the type of paint, so that latex is preferred to enamel. You can then assign these sequences to a sequence group, and then rank the sequences so that all the colors that are available for a specified type of paint are sequenced, or all the types of paint that are available for a specified paint are sequenced, according to the ranks of the sequences in the sequence group.
Box 3: Master planning
Enable the sequence planned orders parameter
Master plans overview
Sequencing
Sequencing enables planned orders to be arranged based on sequencing attributes that are associated with the finished product. It's often used to prepare production orders for packaging. For example, it can be used to pack boxes in a specific sequence, based on color and size.
By setting the Sequencing option to Yes, you can specify how far in the future the operations or jobs should be sequenceD. Keep in mind that the longer the time fence is, the longer it will take for master planning to run.
Reference:
https://ellipsesolutions.com/dynamics-365-boms-formulas-whats-deal/
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dynamicsax-2012/appuser-itpro/about-batch-order-sequencing
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dynamicsax-2012/appuser-itpro/set-up-sequence-groups
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dynamics365/supply-chain/master-planning/master-plans