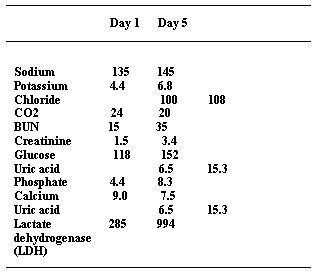
A 53-year-old Black male, with a history of hypertension, hepatitis C, and newly diagnosed nonsmall cell lung cancer, undergoes his first round of chemotherapy, which includes cisplatin. You are called to see this patient 5 days into his hospitalization for oliguria and laboratory abnormalities. Other than the chemotherapy, he is receiving lansoprazole, acetaminophen, and an infusion of D5-- 0.9% normal saline at 50 mL/h. On examination, his BP is 98/60 and heart rate is irregular, between 40 and 50 bpm. His physical examination shows a middle-aged male in no acute distress. His cardiac examination is unremarkable, his lungs show bibasilar crackles, and the abdominal examination is positive for a palpable spleen tip without any hepatomegaly or abdominal tenderness. He has trace bilateral ankle edema. His distal pulses are irregular. The neurologic examination was unremarkable. His laboratory (serum sample) results are as follows
What is the most likely etiology of this patient's acute renal failure?
- renal tubular deposition of uric acid
- calcium oxalate kidney stones causing partial urinary tract obstruction
- renal tubular injury due to cisplatin
- ischemic acute tubular necrosis from a decreased cardiac output
- type II cryoglobulinemia due to hepatitis C
Answer(s): A
Explanation:
The patient has tumor lysis syndrome. The destruction of malignant cells by chemotherapeutic agents will lead to the release of intracellular contents, including potassium, phosphorus, and uric acid (from nucleic acids). This can result in hyperkalemia, hyperuricemia, and hyperphosphatemia. Hyperkalemia will produce significant ECG abnormalities, including peaked T waves and widened QRS complexes. The presence of bradycardia and irregular heart rate on physical examination are suggestive of the cardiac effects of hyperkalemia, which can lead to lifethreatening arrhythmias if not addressed. Patients with tumor lysis syndrome can develop a severe hyperuricemia. The kidneys are responsible for the excretion of uric acid. In acidic urine, the uric acid can crystallize in collecting tubules, resulting in intratubular obstruction and acute kidney failure. Calcium oxalate stones are not a part of this entity. Cisplatin can cause renal potassium and magnesium losses, which is not the case in this patient. The laboratory data suggest the release of intracellular contents (high LDH, uric acid, potassium, and phosphate) and the diagnosis of urate nephropathy as the cause of his acute kidney failure. As mentioned before, hyperkalemia will produce significant ECG abnormalities, including peaked T waves and widened QRS complexes. Prominent U waves are found in hypokalemia, not hyperkalemia. Atrial fibrillation is not typically seen in hyperkalemia