Apatient you see routinely in the clinic has elevated liver function tests. ALT is 89, AST is 75, and the total bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase are normal. The patient has no past history of hepatitis, taking medications, or excessive drinking. You order hepatitis serologies. The results are as follows: Positive:
HBsAg and anti-HBc. Negative: anti-HBs, anti-HBc IgM, anti-HAV, and anti-HCV Which statement best describes this clinical situation?
- If the patient was found to be HBe antigen positive, he would be considered highly infectious to spread hepatitis B
- This patient is in the "window period" because the antibody to hepatitis BsAg is negative.
- This patient is not at risk for delta hepatitis because the patient has antibody to hepatitis B core.
- The low level of transaminase elevations indicates that this patient is not a candidate for hepatitis B antiviral treatment.
- If this patient has antibody to hepatitis Be, he is a candidate for antiviral therapy.
Answer(s): A
Explanation:
This patient has chronic hepatitis B. The different serologic studies for hepatitis B are shown in two figures below. The patient does not have acute hepatitis B because the IgM antibody to hepatitis B core is negative, and the total antibody to hepatitis B core is positive. Antibody to hepatitis B core occurs prior to the development of antibody to hepatitis B surface. IgM is found in acute infections; primarily IgG is seen in chronic infections.
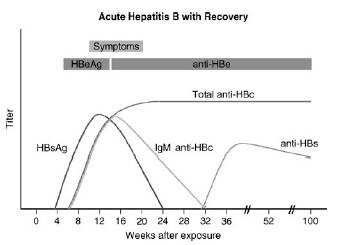
The presence of antibody to
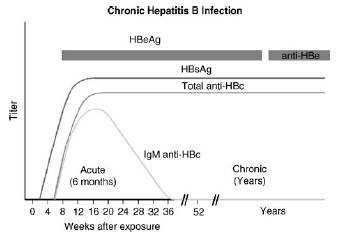
hepatitis B core with a positive hepatitis B surface antigen is indicative of chronic infection. Delta hepatitis infection requires the hepatitis B surface antigen. Delta hepatitis can occur concurrently with acute hepatitis B infection or later in the setting of chronic hepatitis B infection. There is no test for hepatitis C antigen. This is not a presentation of acute hepatitis A, which usually has very high transaminases. The antibody to hepatitis A virus occurs after 1 month and is associated with high transaminases Hepatitis Avaccine is indicated for patients with chronic liver disease. If this patient had hepatitis C, then hepatitis B vaccine would also



be indicated. Hepatitis B vaccine is essentially hepatitis B surface antigen that causes the production of hepatitis B surface antibody. Since this patient has hepatitis B surface antigen already, choice C would be incorrect. Verifying the diagnosis with a qualitative hepatitis B viral load is not necessary. A quantitative hepatitis B viral load might be useful to evaluate for potential antiviral therapy. The only reason hepatitis Awould be recommended for the patient's spouse would be if the patient had acute hepatitis A. Investigating for other causes of hepatitis is not necessary as the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis B is already established.
If the patient was found to be HBeAg positive, he would be considered highly infectious for the spread of hepatitis B. Hepatitis Be antigen is the DNA polymerase that shows active replication of the hepatitis B virion. These patients are 100 times more infectious than those lacking the hepatitis Be antigen. The window period is a situation where a patient is just recovering from hepatitis B. Hepatitis Bs antigen is negative and the antibody to hepatitis Bs has not been developed. The diagnosis is made by antibody to hepatitis B core. This is seen in Figure 1-6. Any patient who is hepatitis B surface antigen positive is at risk for delta hepatitis. This patient would be at risk for delta hepatitis by virtue of having a positive hepatitis B surface antigen. There is no level of transaminases, even normal transaminases, which would preclude antiviral therapy. The level of viral production indicated by the hepatitis B quantitative viral load, along with an assessment of the underlying liver pathology, is the best indication of need for treatment. As mentioned earlier, the antibody to hepatitis B would show the patient is less infectious and likely have a lower viral load.