A bank plans to open a branch in one of five locations (labeled L1, L2, L3, L4, L5). Demand for bank services may be high, medium, or low at each of thes e locations Profits for each location- demand combination are presented in the payoff matrix.
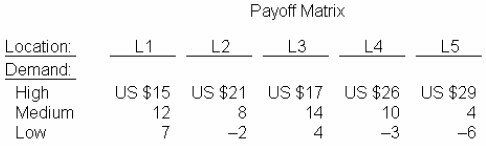
If the bank uses the minimax regret criterion for selecting the location of the branch. it will select:
Answer(s): B
Explanation:
Under the minimax regret criterion, the decision maker selects the choice that minimizes the maximum regret (opportunity cost). The maximum regret for each location is determined from the opportunity loss matrix.