HOTSPOT (Drag and Drop is not supported)
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure key vault named Vault1.
You deploy Azure Disk Encryption.
You configure Vault1 to support Azure Disk Encryption.
You need to ensure that you can encrypt Azure Disk Encryption artifacts before they are written to Vault1. The solution must provide the highest level of encryption.
How should you complete the command? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
Note: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

- See Explanation section for answer.
Answer(s): A
Explanation:

Box 1: key
Create and configure a key vault for Azure Disk Encryption on a Windows VM
Set up a key encryption key (KEK)
If you want to use a key encryption key (KEK) for an additional layer of security for encryption keys, add a KEK to your key vault.
When a key encryption key is specified, Azure Disk Encryption uses that key to wrap the encryption secrets before writing to Key Vault.
Use the Azure CLI az keyvault key create command to generate a new KEK and store it in your key vault.
az keyvault key create --name "myKEK" --vault-name "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" --kty RSA --size 4096
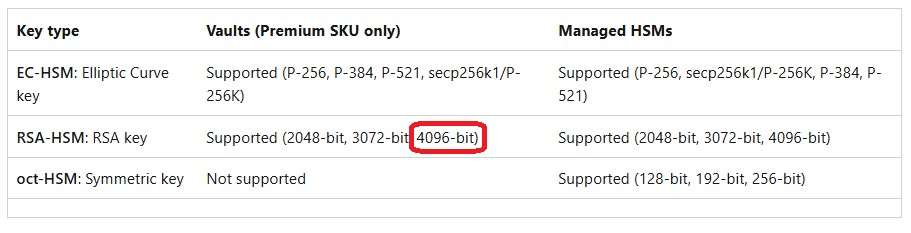
Box 2: RSA-HSM
For 4096-bit encryption choose RSA-HSM.
Note: Which to choose
For maximum key security: Always use an HSM (like EC-HSM or RSA-HSM) to protect your keys, regardless of the algorithm you choose.
Key types and protection methods
Key Vault Premium and Standard support RSA and EC keys. Managed HSM supports RSA, EC, and symmetric keys.
HSM-protected keys
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/windows/disk-encryption-key-vault https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/key-vault/keys/about-keys