A company} is formulating its plans for the coming year, including the preparation of its cash budget. Historically, 30% of the company's sales are cash sales. The remaining 70% are credit sales with the following collection pattern.
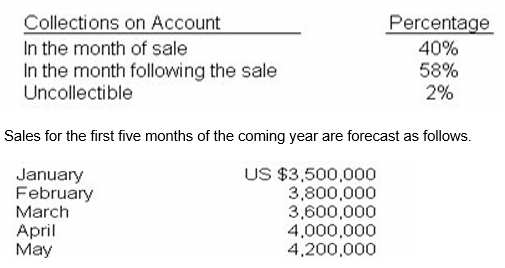
For the month of April, the total cash receipts from sales and collections on account would be:
- US $3,729,968
- US $3,781,600
- US $4,025,200
- US $4,408,000
Answer(s): B
Explanation:
The cash receipts for April equal April's cash sales US $4,000,000 x 30°l0 = US $1,200,000), 40% of April's credit sales, and 580/o of March's credit sales. Consequently, total cash receipts equal US $3, 78-1,600 [$1,200,000 + $4,000,000 40°lax 70°/o) + $8,600,000 68°f0 70%)].A bank has two drive-in lanes to serve customers: one attached to the bank itself and one on an island. One teller serves bath stations. The bank is interested in determining the average waiting times of customers and has developed a model based on random numbers. The two key factors are the time between successive car arrivals and the time customers wait in line. Assume that the analysis begins with cars just arriving at bath service windows. bath requiring 3 minutes of service time. Car 1 is the attached window attached to the bank unless that window has more cars waiting than the island window. The lone teller will always serve the car that arrived first. If two cars arrive simultaneously, the one at the attached window will be served before the one at the island.